TM 5-3825-226-24
out by the master cylinder piston causes the caliper
pistons to extend and apply the brakes. When the apply
force is released, a spring returns the master cylinder
piston and the brake fluid returns to the reservoir.
CAUTION: Always bleed air from the hydraulic brake
system when a line has been disconnected.
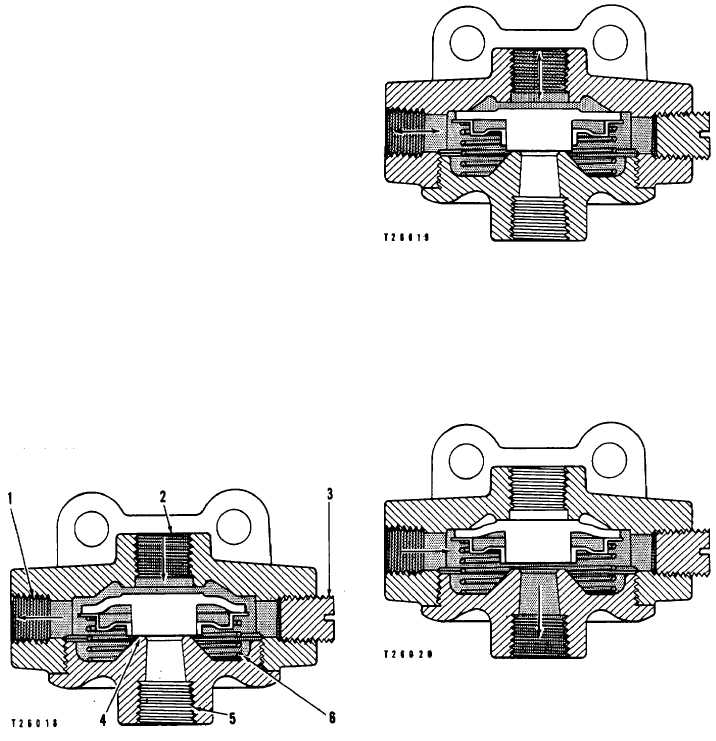
Quick Release Valve
The quick release valve releases the air from the
water distributor rotochamber. The quick release valve
has three positions. In the OPERATE position, pressure
air goes through the valve into the rotochamber. In the
HOLD position, pressure air is held in the rotochamber.
In the RELEASE position, air in the rotochamber is
released through exhaust passage (5).
When the brake pedal is pushed down, pressure air
goes into the inlet passage (2) of the quick release
valve. The diaphragm (4) moves down, closing the
exhaust passage (5). The outer edges of the diaphragm
are pushed down against the resistance of spring (6).
Pressure air goes through the outlet passage (I) to the
rotochamber.
QUICK RELEASE VALVE
(OPERATE POSITION)
1. Passage to rotochamber. 2. Inlet passage. 3. Plug.
4. Diaphragm. 5. Exhaust passage. 6. Spring.
When the pressure below the diaphragm is the
same as the pressure above the diaphragm, spring (6)
moves the edge of the diaphragm up against the valve
body. The center of the diaphragm still covers the
exhaust passage (5). This is the HOLD position.
QUICK RELEASE VALVE
(HOLD POSITION)
When the control valve for the service brakes is
released, air pressure on top of the diaphragm is
released. The air pressure in the rotochambers lifts the
diaphragm and opens exhaust passage (5). Air goes out
of the rotochambers through passage (1) to release the
brakes.
QUICK RELEASE VALVE
(EXHAUST POSITION)
Wheel Brakes
The friction pad (3) is pushed against disc (6) to
provide brakes for the machine. The discs turn with the
wheel hubs, and the calipers are connected solidly on
the axle flange. The brake assembly has two pistons
and a friction pad on each side of the disc. The pads
and backing are held in place by anchor pins. When
there is a brake application, oil, pushes the piston and
pads against the disc.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to pistons and seals, do
not push on brake pedal when brake pads are removed.
2-135