INTRODUCTION
Dependable performance can be expected from a Perkins marine diesel engine when the operation and maintenance
procedures are based upon a clear understanding of diesel engine operating principles. Each moving part of the engine
affects the operation of every other moving part and the engine as a whole.
Perkins diesel engines are four stroke cycle engines with either a direct or indirect combustion system. Diesel engines
differ from other internal combustion engines in several ways. Compression ratios are higher than in gasoline engines.
The intake stroke provides air only to the cylinder. Fuel is delivered to the cylinder in an atomized form by an injector.
This fuel, in accurately metered quantities and with exact timing, is delivered to the injectors via extremely high pressure
from the fuel injection pump. Ignition of the fuel is effected by the heat developed from compressing the air into the
combustion chamber.
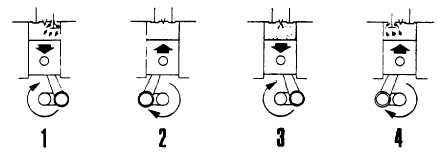
PERKINS DIESEL FOUR STROKE CYCLE
1. INTAKE STROKE - The piston travels down the cylinder, the intake valve is open and the exhaust valve is closed.
The partial vacuum created by the downward stroke of the piston pulls air from outside through the open intake valve
into the cylinder.
2. COMPRESSION STROKE - At the end of the intake stroke, the intake valve closes while the piston travels upward on
the compression stroke. The exhaust valve remains closed. At the end of the compression stroke, the air in the
combustion chamber has been forced by the piston into a space that is one-sixteenth (or less) the original volume
available at the beginning of the stroke. Thus, the compression ratio is 16:1 (or, for some engines, greater).
Compressing the air into a small space causes the temperature to rise to approximately 1000 degrees F. Just before
T.D.C., a small atomized, metered charge of fuel is injected into the combustion chamber, the fuel is ignited by the hot
air and starts to burn.
3. POWER STROKE - During the power stroke, the piston travels down the cylinder and both intake and exhaust valves
are closed. As the air and fuel mixture burns, the gases become hotter and hotter, rapidly expand and add force to
crankshaft rotation.
4. EXHAUST STROKE - During the exhaust stroke, the intake valve remains closed, the exhaust valve is open, and the
piston on the upward stroke forces the burned gases out of the combustion chamber through the open exhaust valve
port.
Turbocharged engines utilize the exhaust to power the turbine and "boost" the density of the intake air, which results in an
increase in engine power.
The standard direction of rotation for Perkins marine diesel engines is counterclockwise when viewing the engine from the
gearbox end (rear) of the engine. Contrarotating engines (rotation is clockwise when viewing the engine from the rear)
are the exception.
-4-