TM 5-3825-226-24
BASIC BLOCK
CYLINDER BLOCK
The cylinders are a part of the cylinder block. There are
no replaceable cylinder liners. The cylinders can be
machined (bored) up to .040 in. (1.02 mm) oversize for
reconditioning. The cylinders in the block are at a 90°
angle to each other. There are five main bearings in the
block to support the crankshaft.
CYLINDER HEAD
There is one cylinder head for each side (bank) of the
engine. One intake and one exhaust valve is used for
each cylinder. The valve guides are a part of the
cylinder head and can not be replaced. A valve seat
insert is used for the exhaust valve and can be
replaced. When the seat for the intake valve has been
machined to the limits given in the SPECIFICATIONS, it
can be bored (machined) for a valve seat insert.
PISTONS, RINGS AND CONNECTING RODS
The pistons have two rings which are located above the
piston pin bore. There is one compression ring and one
oil control ring. The oil ring is made in one piece and
has an expansion spring behind it. The compression
ring is also one piece and goes into an iron band that is
cast into the piston.
The piston pin is held in the piston by two snap rings
which go into grooves in the piston pin bore.
The connecting rod is installed on the piston with the
boss on the connecting rod on the same side as the
crater in the piston. The connecting rod bearings are
held in location with a tab that goes into a groove in the
connecting rod.
CRANKSHAFT
The force of combustion in the cylinders is changed to
usable rotating power by the crankshaft. The crankshaft
can have either six or eight counterweights. A gear on
the front of the crankshaft turns the engine camshaft
gear and the engine oil pump. The end play of the
crankshaft is controlled by the thrust bearing on No. 4
main bearing.
VIBRATION DAMPER
The twisting of the crankshaft, due to the regular power
impacts along its length, is called twisting (torsional)
vibration. The vibration damper is installed on the front
end of the crankshaft. It is used for reduction of
torsional vibrations and stops the vibration from building
up to amounts that cause damage.
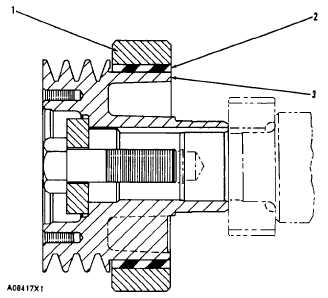
The damper is made of a flywheel ring (1) connected to
an inner hub (3) by a rubber ring (2). The rubber makes
a flexible coupling between the flywheel ring and the
inner hub.
CROSS SECTION OF A VIBRATION DAMPER
1. Flywheel ring. 2. Rubber ring. 3. Inner hub.
2-18